Tribal TAB
Supporting Indigenous communities in protecting and restoring sacred lands.
The Tribal Technical Assistance to Brownfields (Tribal TAB) program supports Indigenous communities in protecting and restoring sacred lands and accomplishing revitalization goals through the reuse, restoration, or redevelopment of brownfields.
By providing collaborative, culturally-informed assistance and resources, practical tools, and a meaningful network of peers, mentors, and subject-matter experts, Tribal TAB equips Tribal Nations and tribal entities to address brownfields, build strong Tribal Response Programs, and enhance self-governance opportunities, while protecting and preserving the local environment.
Tribal Brownfields Knowledge Circle (TBKC)
The Tribal Brownfields Knowledge Circle (TBKC) is a community of practice for Tribal environmental professionals working at the confluence of Indigenous lands, brownfields revitalization, healthy communities, and cultural resilience. This group is a Tribal-only space, open exclusively to staff from Tribes, Native Villages, and Tribal consortia. Join the mailing list to receive newsletters and invitations to our events..
TBKC Forum
The Tribal Brownfields Forum is a virtual gathering space designed to bring together Tribal environmental professionals and others working in the Tribal brownfields sphere. This community-supported space offers a place to ask questions, share knowledge, exchange ideas, and learn from one another.
TBKC Events
Participate in the TBKC community through our regular online conversations In a Good Way Chats or at one of our annual in-person events such as the Brownfields Site Visit or the Tribal Lands Environment Forum. Join the TBKC listserv to receive invitations for these and other gatherings.
Other TAB Providers
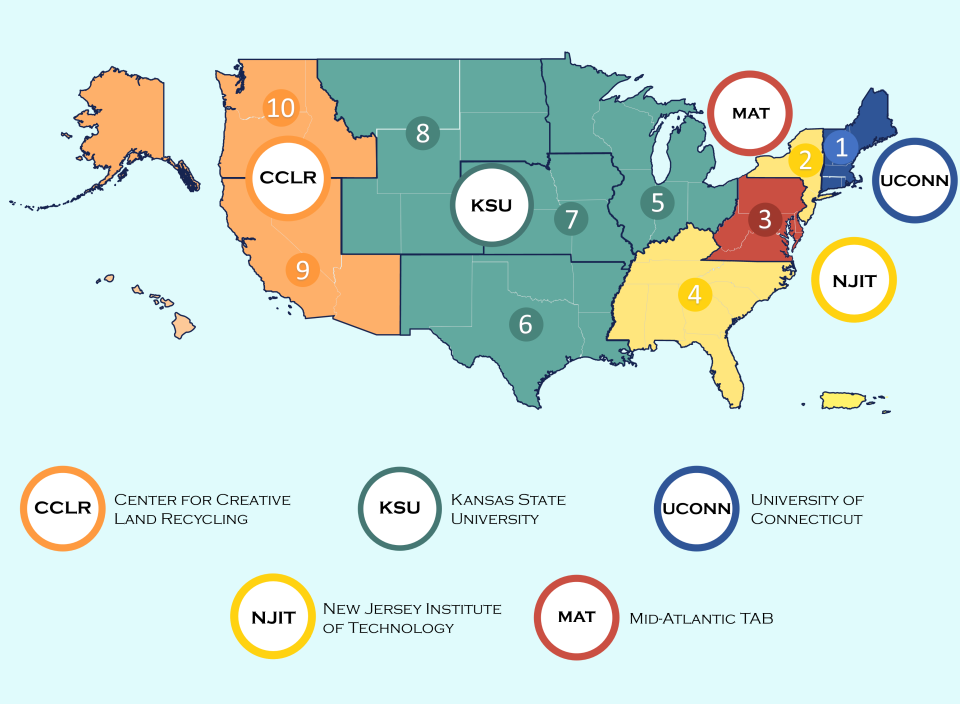
EPA has awarded TAB Grants which provide technical support to brownfield sites in multiple EPA regions as listed below. See EPA’s Brownfields Technical Assistance webpage to learn more about the current awardees.
-
- EPA Region 1: The University of Connecticut
- EPA Region 2: New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT)
- EPA Region 3: The West Virginia University Research Corporation,
- EPA Region 4: The International City/County Management Association
- EPA Regions 5, 6, 7, 8 and nationwide: Kansas State University (KSU)
- EPA Regions 9 and 10: Center for Creative Land Recycling (CCLR)
